Taxation in Tally
All Accounting Taxation like TDS, Service Tax, VAT and CST and Excise
Service Tax in Tally.ERP 9
For notes in PDF Click here
TDS in Tally ERP 9
VAT in India
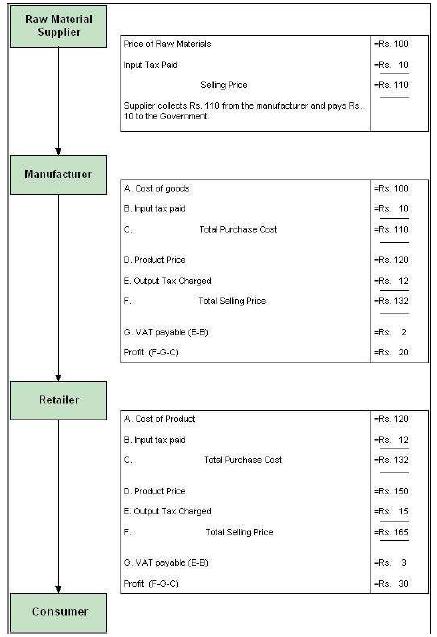
The Value Added Tax (VAT) is a type of indirect tax and is one of major source of revenue to the state. The VAT system was introduced in India by replacing the General Sales Tax laws of each state. Presently in India, out of 35 States and Union Territories, 32 are following this new system of Sales Taxation. The States/Union territories which are yet to implement the VAT system are Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Nagaland and Lakshadweep.
The VAT system of taxation was adopted by Indian States and Union Territories in the Year 2005 by replacing the General Sales Tax Laws with New Value Added Tax Acts and the supporting Value Added Tax Rules for proper administration and collection of Tax. Each state or union territory has its own methods to assess the tax liability and collection methods from the dealers who fall under the purview of VAT.
The Administration of VAT system was undertaken by the Commercial Taxes Department of each state along with the Excise and other indirect taxes. For easy and quick assessment of taxation and prevention of tax evasion, the department has introduced the Registration System. This Registration system of VAT helps in identifying the assessees who come under purview of VAT and are liable to collect and pay VAT. For encouraging the Registration process some benefits or concessions are given to the dealers.
The Registered dealers are allowed to collect VAT payable by them from the immediate buyer. They can claim the VAT paid on purchases made only from a registered dealer. The unregistered dealer cannot charge VAT on the invoices, so the buying dealer cannot claim the VAT amount paid as ITC. Also, the unregistered dealers are not eligible for availing concessions, for e.g., exemptions, which are given by the government.
The commercial tax department introduced a new method of levying tax called as the Composition Scheme especially after considering the small dealers whose turnover was low and were unable to maintain the records as per the requirements of VAT Act. These dealers have to pay a lump sum as VAT on the sale value of goods. The VAT paid will not be shown in the invoices. They can account for the total turnover and pay VAT on the same at the end of the return period.
For Assessing the VAT liability of dealers, each state has introduced the system of Filing Returns for different tax periods. The tax periods could be Monthly, Quarterly, Half-yearly and Annual. Each dealer has to file the Return by specifying the total turnover which is exempted as well as liable for VAT along with the purchases made and tax paid on it with the amount of VAT payable or Input tax credit carried forward within the stipulated period.
For General Tally Terminologies related to VAT Click here
How to account TDS deducted by your customer
When we raise an invoice to our client, on which our client is requires to deduct TDS and pays the balance amount to us. The amount so deducted by our client, he is liable to pay it to the Income Tax department within first week of next month, hence its a receivable for us which we have to claim from the Income Tax Department and not from our client.
Now, we will see how to handle this situation in Accounts and Tally ERP 9 ?
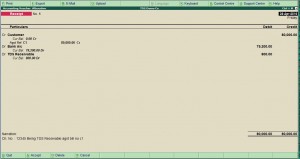
Suppose we  have issue a bill of Rs. 80000 on which Customer deducted TDS of Rs. 800 and pays you Rs. 79200 back to us. Then the entry in your books will be as under :
| Particulars | Amount |
| Dr. Bank Account | Rs. 79200 |
| Dr. TDS Receivable Account | Rs. 800 |
| Cr. Customer | Rs. 80000 |
( This ledger should be open under the Group Loans & Advances (Asset))
The result will be that your customer a/c will be settled off and the TDS amount will be shown as receivable in the Balance sheet which we have to claim from the Income Tax department. We will get Form No. 16A From our client in this regard in support of our claim.
How to apply Lower Deduction TDS Rates for certain supplier
How to use lower deduction TDS rates for certain suppliers
By virtue of Section 197/197A an assesses can get a certificate of lower deduction from the ITO.
Such certificate will include your TAN number, Assesses PAN Number, Period of applicability, approx. billing amount to you during the period and the % of TDS by which you should deduct TDS on the same.
Let’s assume one of your supplier presents you such a certificate of lower deduction of tds at a rate of 6%, then you must deduct the same as per the certificate produced to you.
Let’s learn how to manage the same in Tally.ERP 9. Once you make the settings as per below then whenever you book the invoice of such supplier then TDS will be calculated and deducted from the bill automatically at the rates specified as per the lower Deduction certificate
- Go to related supplier’s ledger who produced you the lower deduction certification
- (Note : Enable “Allow ADVANCED entries in TDS Master†form F12 configuration)
- Enable “ Is TDS Deductable�
- Deductee Type : select deductee type from the list
- Use Advanced TDS Entries : Set to “Yesâ€
- You will find a pop up as per below

- Enable “ Set Zero/Lower Deductionâ€Â to “Yesâ€
- You will find below screen

- Select the Nature of payment applicable from the pop up window list
- Set section number (it will be shown in the lower deduction certificate
- Mention necessary details and save it.
If you are not aware of TDS features in tally then you should referTDS help file for further reference