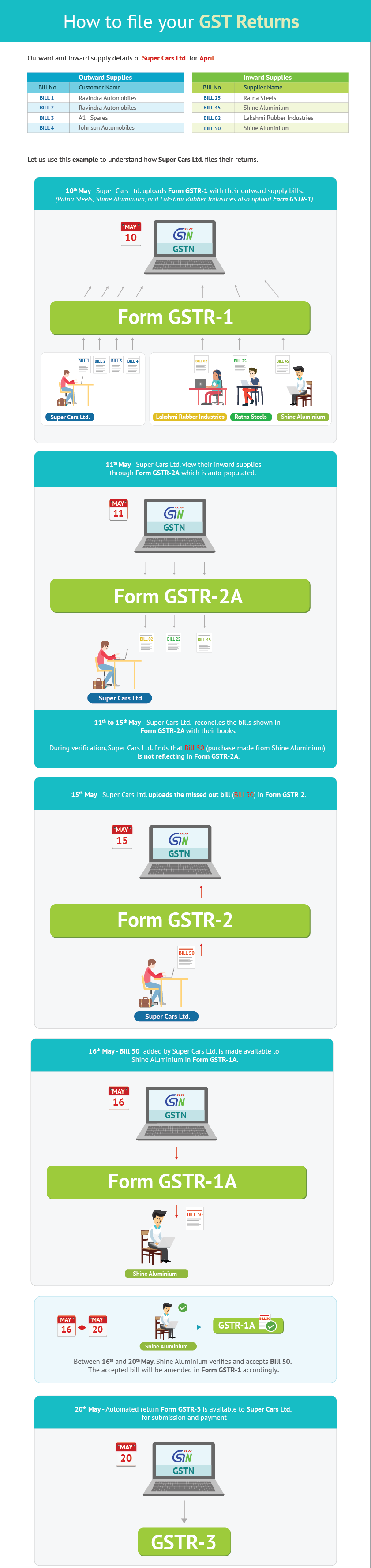
Every registered taxable person has to furnish outward supply details in Form GSTR-1 by the 10th of the subsequent month. On the 11th, the visibility of inward supplies is made available to the recipient in the auto-populated GSTR-2A. The period from 11thto 15th will allow for any corrections (additions, modifications and deletion) in Form GSTR-2A and submission in Form GSTR-2 by 15th of the subsequent month.The corrections (addition, modification and deletion) by the recipient in Form GSTR-2 will be made available to supplier in Form GSTR-1A. The supplier has to accept or reject the adjustments made by the recipient. The Form GSTR-1 will be amended according to the extent of correction accepted by supplier.
On 20th, the auto-populated return GSTR-3 will be available for submission along with the payment. After the due date of filing the monthly return Form GSTR-3, the inward supplies will be matched with the outward supplies furnished by supplier, and then the final acceptance of input tax credit will be communicated in Form GST ITC-1.
Also, the mismatch input tax credit on account of excess claims or duplication claims will be communicated in Form GST ITC-1.Discrepancies not ratified will be added as output tax liability along with interest. However, within the prescribed time, if it is ratified, the recipient will be eligible to reduce this output tax liability.
Let us understand this with an example.