On the 4th of May, 2018, the 27th GST Council meeting got underway, giving shape to the new returns filing model, which was awaited for the past several months. The new model was decided, based on the recommendations of the Group of Ministers, which had been constituted for the purpose of making the process a simplified one on the 17th of April, 2018. In addition the GST Council also did announce a few rate changes, and some structural changes in the shareholding pattern of the GSTN.Let’s go through all the major 27th GST Council meeting highlights:
27th GST Council meeting – Simplified returns
The 27th GST Council meeting introduced a simplified return filing process, major features of which are as follows:
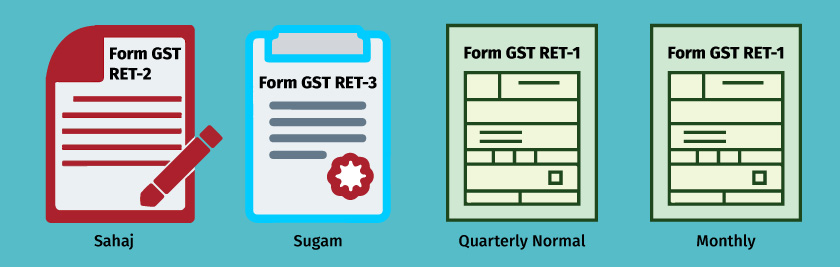
One monthly return
All taxpayers, with a few exceptions, will have the facility to file one monthly returns, and the return filing dates will be determined in a staggered order, based on the turnover of the registered person. This has been primarily done to manage the load on the GST portal. Composition dealers and dealers with nil transactions will continue to file quarterly returns, as per the 27th GST Council meeting highlights.
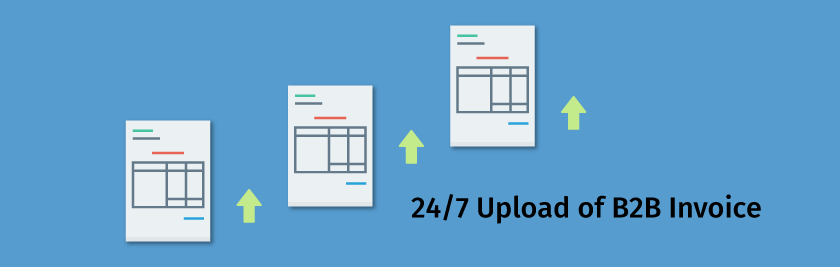
Unidirectional flow of bills
There shall be a unidirectional flow of bills, i.e. bills may be uploaded by the seller anytime during the month, which will serve as valid documents to avail input tax credit for the buyer. The buyer too, will be able to see the uploaded invoices on a continuous basis, during a particular month. There will be no need to upload any purchase invoices as per the model suggested initially. Also, for all B2B transactions, HSN codes of 4 digits or more will need to be specified to achieve uniformity in the reporting system, as per the 27th GST Council highlights.
Simpler returns design
B2B dealers will need to fill invoice wise details of all outward supplies made by them, based on which the system will automatically calculate their tax liability. Similarly, their input tax credit will be calculated automatically by the system based on the invoices uploaded by their sellers. All this will be supported by a user-friendly interface coupled with an offline tool to upload invoices. Another major aspect of simplifying the returns process introduced by the 27th GST Council meeting was, the reduction in the content or the information required to be filled in the return forms. The details of the design of the return form, business processes and legal changes will be worked out by the appointed law committee based on these principles, as per the 27th GST Council updates.
No automatic reversal of ITC
There shall not be any automatic reversal of input tax credit from the buyer, in case the seller does not pay the tax, as was the case earlier. In case the seller defaults on the payment of tax, the recovery shall be made from the seller itself. However, as per the 27thGST Council recommendations, the option of reversal of ITC from the buyer shall also be an option available to the GST authorities, to address exceptional scenarios, such as, missing dealers, closure of business by the supplier, supplier not having adequate assets etc.
Online process for recovery and reversal
The recovery of tax or reversal of ITC shall be done through an online and automated process to reduce the human interface. The process will continue to follow the due course of issuing a notice and order, as per the updates from 27th GST Council meeting.
Supplier side control
In case a supplier has defaulted in payment of tax above a threshold amount, such a supplier will not be allowed to upload invoices and thus will not be allowed to avail any ITC. This has been introduced to avoid and to control misuse of the ITC facility. Similar safeguarding provisions have now been built in for newly registered dealers as well as per the 27th GST Council meeting updates. The GST Council has proposed setting up analytical tools to identify such transactions at the earliest, so that loss in revenue may be prevented.
Three stage transition
The following 3 stage transition to the new returns filing system was decided upon at the 27th GST Council meet:
- Stage 1 – Present system of filing GSTR 3B and GSTR 1 returns. GSTR 2 and GSTR 3 will remain suspended. This will continue for a maximum of 6 months, by which the new return filing software will be ready.
- Stage 2 – New return system will go live, with the facility for invoice – wise data upload and also facility for claiming ITC on a self-declaration basis, similar to the role of GSTR 3B currently. During this stage, the dealer will be constantly fed with information about the existing gap between ITC available, and provisional ITC being claimed.
- Stage 3 – Provisional credit will get withdrawn totally, and ITC will be limited only to the invoices uploaded by the sellers from whom the dealer has purchased goods.
GST Rates discussed at the 27th GST Council meeting
While there were no GST rate changes announced as such at the 27th GST Council meeting, there was a good deal of discussion on the following two aspects:
- Reduction of GST rates for digital transactions – Keeping in mind the need to move towards a less cash economy, the GST Council discussed a proposal to have a concession of 2% in the GST rate i.e. 1% each for CGST and SGST, for all B2C supplies in which payments are done via cheque or via digital mode. This was proposed in all cases where the overall GST rate is more than 3%, with a ceiling of INR 100 per transaction. The GST Council has recommended to set up a Group of Ministers from the State Governments to look into the proposal and make recommendations, before the next GST Council meeting, as suggested by the 27th GST Council meeting news.
- Sugar Cess over and above 5% GST and reduction in GST rates of ethanol – Keeping in mind, the record production of sugar in the current sugar season, and the consequent reduction in sugar prices, the GST Council discussed imposing a sugar cess over and above the stipulated 5% GST rate and also considered reducing the GST rate on ethanol. The proposal has come from the food ministry, which has been mulling cutting down the GST rates on ethanol to help sugar mills clear dues worth INR 19,000 crore to sugarcane farmers. However, a conclusion could not be reached, and the GST Council finally recommended to set up a Group of Ministers from the State Governments to look into the proposal and make recommendations, within a period of 2 weeks, as per the 27th GST Council news.
GSTN changes finalised at the 27th GST Council meeting
The GSTN, as one may be aware, was created as a private limited, non-profit company, with an objective to provide shared IT infrastructure and services to Centre and State governments, tax payers and other stakeholders for the implementation of GST. Currently, the Central government and State governments are holding 24.5% equity shares respectively and the remaining 51% are held by 5 non-governmental institutions namely – HDFC, HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, NSE Strategic Investment Co and LIC Housing Finance Ltd. Majority of the GST processes including registration, return filing, tax payment, refunds processing are largely IT driven, and thus it was a given that the GSTN was handling large scale invoice level data of lakhs of business entities.
Considering the nature of the functions handled by GSTN, the GST Council felt that the GSTN should be converted into a fully owned government company.
Keeping this in mind, it was decided at the 27th GST Council meeting, that the 51% held by the non-governmental institutions, worth INR 5.1 Crore, was decided to be distributed equally among the Centre and the State governments, thus taking the respective share of both bodies to 50% each. It was also decided that the GSTN board will be allowed to retain the existing staff at the existing terms and conditions for a period of up to 5 years, and shall also have the flexibility to hire people through contract on the terms and conditions similar to those used by GSTN till now, while hiring regular employees. Nevertheless, the existing financial commitments given by the Centre and the States to GSTN to share the capital costs and O&M costs of the IT systems will continue as before.
In short, the 27th GST Council meeting was a major game changer, as far as the simplified return filing process is concerned. Given the various initiatives discussed, proposed and finalised at the meeting, life for the business is surely bound to become simpler as far as GST compliance is concerned.