The new GST return framework has introduced a set of return forms specially designed for small taxpayers. Among the new returns available, Sugam return form is once such GST return aims to simplify the GST complexities.
In this blog, let us discuss and understand Sugam returns, return filing periodicity, tax payment, format and filing process.
What is Sugam GST returns?
Sugam is a new GST return for small taxpayers whose aggregate turnover in the financial year does not exceed 5 Crores and their outward supplies consist of B2B as well as B2C. Businesses opting Sugam GST returns will be allowed to make outward supplies to end consumers, unregistered business and business registered under GST.
Applicability of Sugam return
To opt Sugam return under GST, you need to satisfy the below two conditions.
- The aggregate turnover in the previous financial years is up to 5 crores
- You are engaged in making B2B supplies (Unregistered Business and end consumers) and B2B supplies (supplies to business registered under GST)
Periodicity of filing Sugam return
The periodicity of Sugam return filing is on a quarterly basis with a monthly payment of tax. For businesses opting Sugam GST return, the due date to file a quarterly return is 25th of the subsequent month following the quarter-end.
The due date for filing Sugam GST returns is given below
| Due Date to File Sugam GST Return | |
| Filing Period | Due Data |
| April -June | 25th July |
| July – September | 25th October |
| October- December | 25th January |
| January-March | 25th April |
Due date for payment of tax
Though the return filing periodicity is quarterly, businesses opting Sugam return are required to make the monthly payment.
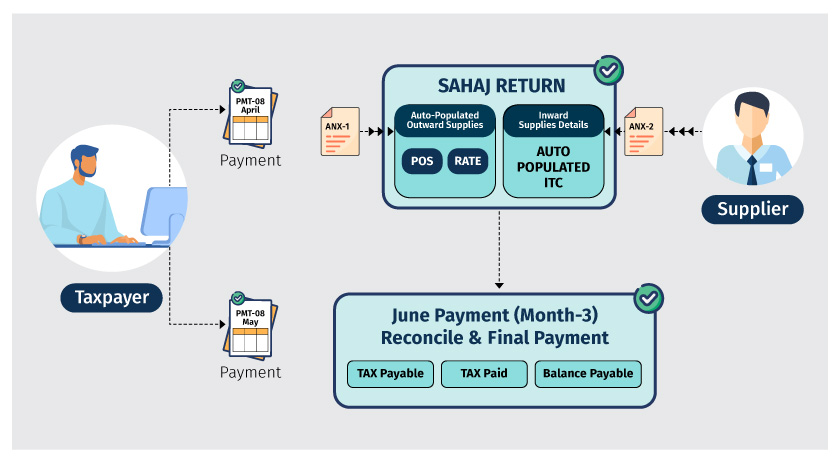
The tax payment is on the self-assessed basis and the payment declaration challan known as Form GST PMT -08 should be used to remit the payment. The due date to remit the monthly payment is 20th of the subsequent month.
Like Sahaj return, the self-assessed payment is required only for 1st and 2nd month of the and for 3rd month, payment with all adjustments should be made along with the returns.
Let’s understand with an example.
For April to June quarter, the taxpayer needs to remit the tax of April by 20th May and May’s tax by 20th June. For June, you need to pay tax along with first 2 months adjustment (if any) with main Sugam returns.
Difference between Sahaj and Sugam GST returns
While both the returns are quarterly and applicable for small taxpayers, basis the supplies nature it supports, these 2 differs. Sahaj as a small taxpayer return supports only B2C supplies whereas Sugam supports B2C as well as B2B supplies.
In other words, Sahaj return is suitable for businesses who are engaged in making only B2C outward supplies. On the other hand, Sugam is suitable for a business who make both B2C as well as B2B supplies.
Types of supplies allowed under Sugam returns
The following table gives the list of supplies allowed and disallowed under Sugam GST returns.
| Type of Outward Supplies | Allowed (Yes) / Disallowed (No) |
| B2B transactions | Yes |
| B2C transactions | Yes |
| Exports | No |
| SEZ units/developers | No |
| Deemed Exports | No |
| Outward Supply to e-Commerce Operators | No |
| Nil Rated, Exempted or Non – GST | Yes |
| Inward supplies attracting RCM | Yes |
| Import of goods/services | No |
| Import of Goods from SEZ | No |
Sugam return filing process
The Sugam GST returns consist of one main return, to be filed on a quarterly basis supported by two main annexures. Form GST RET-3 is the return form to be used to file Sugam returns supported by the annexures.
The details of return forms and annexures to be used for filling Sugam return is given below.
| Form | Description | Action |
| Form GST ANX- I | Form GST ANX-1 is an annexure of outward supplies and inward supplies attracting reverse charge. | You need to upload details of outward supplies along with purchases attracting reverse charge in FORM GST ANX – 1 |
| Form GST ANX – II | It’s an annexure containing details of auto-drafted inward supplies.
|
Form GST ANX-II is an auto-populated annexure containing the details document uploaded by your supplier on a real-time basis.
Here you can either accept, modify or reject the invoice uploaded by your counterpart (seller) for confirming the ITC. |
| Form RET-3 | Form RET-3 is a quarterly return applicable for business opting Sugam returns (Up to 5 Crores) | Business need to file the monthly return by 25th of the subsequent month following the quarter-end |
The key point which businesses should take note is that the option to avail input tax credit on the missing invoices (invoices not uploaded by the supplier) is not available in Sugam returns. This implies that businesses will be allowed to avail the ITC to the extent of the invoices auto-populated in Form GST ANX-II.
However, the option to claim ITC on a provisional basis on the missing invoice is available for taxpayers opting monthly return and quarterly normal return using Form GST RET-1.
Format of Sugam returns – Form GST RET – 03
The Sugam form RET – 03 contains the details of supplies (both inward and outward) declared through Form GST ANX – 1 and GST ANX – 2. This is the main return form which auto-populates the information of supplies from the first two annexure forms. The supplier (taxpayer) needs to complete the remaining details and calculate their tax liability.
To summarize the Sugam return format (Form GST RET-3), it contains the summary level details of outward supplies, inward supplies and adjustments related to it. The Sugam return format consists of the following details:
- Outward supplies
- Inward supplies attracting reverse charge
- Debit/credit notes
- Advanced received
- Total tax liability
- Inward supplies for claiming ITC
- Net ITC available
- Amount of TDS/TCS credit received (Transition / Switchover)
- Interest and late fee (if any) and
- Final payable tax along with details of tax payment and
- Refund claimed from the ledger.