Release Notes – What’s New in TallyPrime
You can count on us for a delightful journey with TallyPrime as we work to enhance the product with new features and fix issues, which will make your experience even simpler and more seamless.
Highlights – TallyPrime Release 2.0
Connected experience for e-Way Bill
With the connected experience for e-Way Bill, TallyPrime enables you to –
- Generate e-Way Bill online at the time of voucher creation.
- Generate multiple e-Way Bills online at one shot.
- Cancel e-Way Bill, update Part B & Transporter ID, and extend validity for transactions in bulk.
- Print e-Way Bill for invoices with e-Way Bill number and QR Code as per the government’s requirements.
- Track the status of e-Way Bills using the e-Way Bill report and e-Way Bill Register.
- Get the latest e-Way Bill information and status from the e-Way Bill system to a transaction using e-Way Bill report and e-Way Bill Register.
As a result, you need not juggle between TallyPrime and the e-Way Bill system for various e-Way Bill activities, as everything can be done from within the product.
Save View for reports
The Save View feature will delight you with a personalized experience for viewing reports in TallyPrime.
You can now:
- Save a preferred view for a report with your desired configurations.
- Save a view for a report for a specific period.
- Save a view for a report opened for a particular master such as Party ledger, Stock Item, and others.
- Save views, as per your requirement, for:
- All companies on a particular computer
- A specific company
- Set a saved view as the default view.
Henceforth, the report will always open as per the configurations applied in the saved view. - Change the default view, whenever needed.
- Delete a saved view or all the views from all companies or a specific company, as needed.
- Restrict users from saving views for reports or deleting views saved in a specific company.
Saving your preferred views saves a great deal of time as you need not apply the configurations time and again.
Online GSTIN/UIN and HSN/SAC validation
TallyPrime is here with a quick and simple process to validate:
- GSTIN/UIN information for single and multiple Parties.
- HSN/SAC information for single and multiple Stock Items.
As a result, you get to know if the information entered in your books is authentic and update it, if needed.
TallyPrime Reports in browsers
Mobile-responsive design
The all-new mobile-responsive design provides you with an intuitive experience right from company selection to downloading a voucher.
Additionally, you can now enjoy the benefits of the following features:
Quick access to change date in Day Book
You can now view Day Book for the previous and next dates by tapping on the left and right arrow keys, respectively.
Scale Factor in selected reports
You can now apply Scale Factor in a report to view the values in hundreds, lakhs, and so on.
Introduction of Show Details
You can now view additional information in selected reports by tapping on Show Details.
Simpler way to change period
You now have a better experience in changing the period of reports in browsers.
File Name of Report downloaded from browser
The file name of the report downloaded from the browser will now have an underscore, which will separate the date and timestamp for easy identification of the date and time of the download.
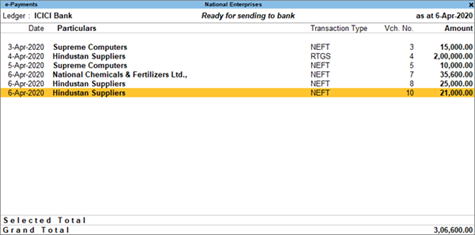
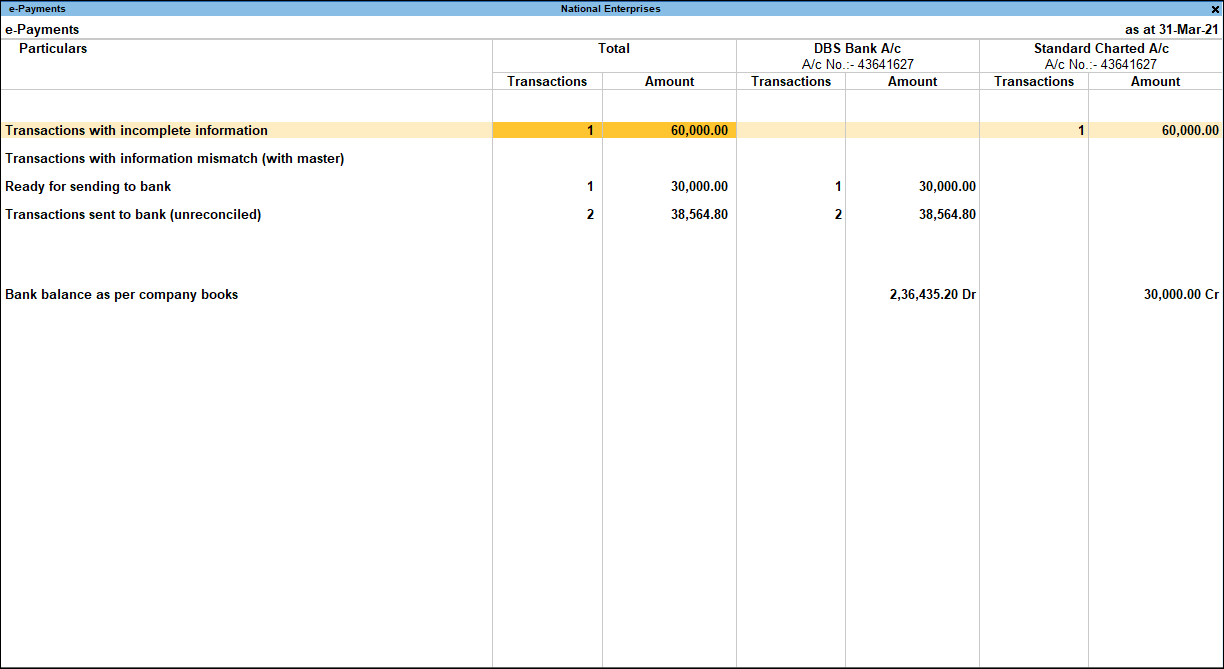
e-Payments in TallyPrime
TallyPrime’s easy-to-use e-payment feature is now extended to RazorpayX Bank and Axis Bank.
Product Improvements – TallyPrime Release 2.0
File your GSTR-1 returns with HSN Summary as per the latest change
As per the latest amendments, in Table 12 of GSTR-1 (HSN Summary) the column Total Value is replaced with the column Rate of Tax. This release of TallyPrime enables you to file your returns with this change.
Party details in exported Ledger Group Outstandings
When you exported the Ledger Group Outstandings report to an MS Excel file, the details of some Parties were missing.
This issue is resolved.
Voucher Register with Verification Status
In the Voucher Register under Verification of Vouchers, the transactions did not appear for the selected Verification Status.
This issue is resolved.
e-Mailing Ledger and Group Outstandings
When you sent Ledger and Group Outstandings to parties via e-mail, the parties that did not have any outstanding amount received a blank report.
This issue is resolved.
GST calculation in sales transactions
When you recorded a sales transaction using Voucher Class, TallyPrime rounded off the tax value with three decimals to two decimals. Consequently, the calculated tax amount was lesser by 1 paisa.
This issue is resolved.
Terms of Delivery in Sales Invoice
Only the first line was visible in Terms of Delivery when you altered a Sales Invoice and provided the Order No.
This issue is resolved.
Performance enhancements in navigation
The performance enhancements in navigation will make your experience with TallyPrime all the more delightful. It will take fewer seconds to:
- Navigate to Credit Note voucher from Gateway of Tally
- Switch between Voucher Types
- Display the List of Ledgers
- Change Buyer Name
- Accept the Supplier Details screen
TCS transactions and reports
The TDL storage error appeared in the TCS transactions and reports, when Use TCS Allocations was enabled in the sales transaction.
This issue is resolved.
Error while uploading Delivery Note on the e-Way Bill system
An error appeared while uploading a Delivery Note on the e-Way Bill system. This happened when you had selected Others as Sub Type while recording the Delivery Note.
This issue is resolved.
Change of ledger in a columnar report
The report details were not getting refreshed when you changed the ledger in a columnar report.
This issue is resolved.
e-Way Bill Number in Multi-Voucher Printing
In multi-voucher printing, the last e-Way Bill number was printed in all the invoices.
This issue is fixed.
TCS Debit Note not linked to TCS Receipt voucher
TCS Debit Notes were not getting linked to TCS Receipt vouchers.
This issue is resolved.
TRN in Sales invoice printed in Arabic
The TRN did not appear when you printed a sales invoice in Arabic.
This issue is resolved.
e-Way Bill number in altered invoice
The e-Way Bill number did not appear in the print when the invoice was altered.
Click here for release notes
Click here for download